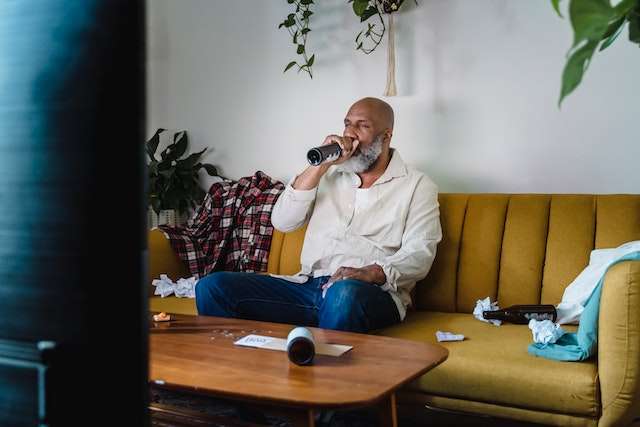
Alcohol addiction is a growing concern in society, impacting individuals and communities across age, gender, and socioeconomic status. Drinking excessively increases your risk of developing a number of issues and can have a variety of negative effects.
This article talks about the importance of recognizing the symptoms and signs of alcohol addiction. The more we learn about these effects, the better prepared we may be to deal with the challenges posed by alcohol abuse, misuse, and dependence.
Understanding AUD (Alcohol Use Disorder), and Alcohol Addiction
Alcohol Abuse and Alcohol Misuse
The terms “alcohol misuse” and “alcohol abuse” refer to the same thing: a pattern of drinking that is unhealthy and goes against safe drinking recommendations.
The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) states that alcohol misuse, which includes binge drinking and heavy drinking, raises your risk of negative effects like AUD (Alcohol Use Disorder).
The NIAA defines binge drinking as drinking enough to raise the blood alcohol concentration (BAC) to 0.08 percent, or 0.08 grams per deciliter. This pattern corresponds to having 5 or more drinks (for men) or 4 or more drinks (for women) in about 2 hours for an average adult.
The risk increases with the number of drinks consumed each day and with alcohol misuse over time. Alcohol addiction is guaranteed.
Alcoholism, AUD (Alcohol Use Disorder), and Alcohol Addiction
Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is a spectrum disorder characterized by an inability to control alcohol use despite adverse social, occupational, or health consequences, often referred to as alcohol abuse, alcohol dependence, or alcoholism. It can be mild, moderate, or severe.
Alcohol addiction is a chronic relapsing disorder associated with compulsive alcohol drinking, the loss of control over intake, and the emergence of a negative emotional state when alcohol is no longer available. Alcohol addiction refers to the moderate-to-severe end of the AUD spectrum.
Why Should We Be Concerned About AUD and Alcohol Addiction?
According to the NIAA, alcohol consumption is associated with a variety of detrimental physical and psychological effects, including interpersonal relationship issues, heart and liver conditions, cancers, auto accidents and other accidents, alcohol poisoning, violence, homicide, and suicide. A person with AUD is more likely to regularly consume alcohol in quantities that result in these health issues, especially if their condition is moderate to severe and involves an alcohol addiction.
Young people are most at risk for AUD. Alcohol use during adolescence (from preteens to mid-20s) may alter how the brain develops and grows, increasing the likelihood that AUD will be identified later in life. However, the majority of people with AUD, regardless of their age or the severity of their drinking issues, can get better with treatment, medication, or both.


Factors Associated with the Development of Alcohol Addiction
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics has a significant impact on one’s susceptibility to alcohol addiction. Due to shared genetic factors that affect brain chemistry and alcohol metabolism, people with a family history of alcoholism are more vulnerable.
Environmental Factors
The environment in which a person is born, raised, and lives in can have an impact on their ability to develop an alcohol addiction. Peer pressure, early alcohol exposure, and a dysfunctional family environment can all have an impact on someone’s relationship with alcohol.
Psychological Factors
Alcohol Addiction frequently interacts with mental health and psychological factors. People may use alcohol as a coping mechanism for stress, trauma, or mental health issues. Personality traits like impulsivity and sensation-seeking can also contribute to the development of alcohol addiction
Common Signs of Alcohol Addiction
Physical Signs of Alcohol Addiction
Increased Tolerance to Alcohol
The body adjusts to consuming more alcohol as alcohol addiction develops. As a result, the person’s tolerance increases, requiring them to consume more alcohol to get the same results they once did with less. This could be an obvious sign that alcohol use is becoming more problematic than just casual.
Depending on the individual, physical symptoms and signs of alcohol addiction can vary, but in the early phases, AUD is frequently characterized by frequent intoxication or a pattern of heavy drinking. .
Other physical signs of alcohol addiction, however, get less attention. These consist of:
- Broken blood vessels on the face and nostrils
- Brittle hair and nails and parched skin due to alcohol dehydration
- An appearance of increased aging and wrinkles
- Poor hygiene
- The persistent odor of alcohol on the breath, even hours after consumption.
- Not eating results in weight loss.
- Yellow skin and eyes due to liver damage
As mentioned, AUD can be classified as mild, moderate, or severe. Depending on their level of alcoholism, a person with AUD might not exhibit all of the mentioned symptoms and signs of alcohol addiction.
Withdrawal Signs of Alcohol Addiction
Individuals addicted to alcohol who attempt to cut back on or stop drinking frequently experience alcohol withdrawal symptoms. These symptoms can range from mild to severe and can include tremors, sweating, nausea, vomiting, anxiety, and even seizures. The presence of withdrawal symptoms can easily identify alcohol addiction.
The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) states that acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms typically appear 6 to 24 hours after the patient has last consumed alcohol. When a patient still has significant blood alcohol levels, alcohol withdrawal may start. The following are possible withdrawal symptoms and signs of alcohol addiction:
- Restlessness, irritability, anxiety, agitation
- Anorexia (lack of appetite), nausea, vomiting
- Tremor (shakiness), elevated heart rate, increased blood pressure
- Insomnia, intense dreaming, nightmares
- Poor concentration, impaired memory and judgment
- Increased sensitivity to sound, light, and tactile sensations
- Hallucinations (auditory, visual, or tactile)
- Delusions, usually of paranoid or persecutory varieties
- Grand mal seizures (grand mal seizures represent a severe, generalized, abnormal electrical discharge of the major portions of the brain, resulting in loss of consciousness, brief cessation of breathing, and muscle rigidity followed by muscle jerking; a brief period of sleep, awakening later with some mild to even severe confusion, generally occurs)
- Hyperthermia (high fever)
- Delirium with disorientation with regard to time, place, person, and situation; fluctuation in level of consciousness.
Behavioral Signs of Alcohol Addiction
Drinking Alone or Secretly
When a person drinks alone or makes an effort to conceal their drinking from others, this is one obvious behavioral sign of alcohol addiction. This behavior often arises from a sense of shame or fear of judgment.
Failed Attempts to Quit or Cut Down
Individuals with alcohol addiction may make repeated attempts to quit drinking or reduce their consumption, but they frequently fail. This pattern might indicate a loss of control over alcohol consumption.
Neglecting Obligations and Responsibilities
People who are dependent on alcohol may put drinking before their duties and commitments, including those to their families, jobs, and personal lives. Neglecting these areas of life can lead to deteriorating relationships, job loss, and overall instability.
Neglecting Hobbies and Social Activities
As alcohol addiction takes hold, people frequently start to lose interest in their hobbies and other past interests. They might also avoid non-drinking social gatherings, which would isolate them.
Psychological Signs of Alcohol Addiction
Alcohol Cravings and Preoccupations
Intense cravings for alcohol and a persistent obsession with obtaining and consuming it are characteristics of alcohol addiction. These cravings may become too strong, making it difficult to concentrate on other facets of life.
Irritability, Mood Swings, and Anxiety
Addiction to alcohol can lead to emotional instability and mood swings. People may display heightened irritability, frequent mood swings, and increased anxiety even when sober.
Denial of the Problem
Denial is a common coping mechanism for people with alcohol addiction. Individuals might downplay the severity of their drinking or its consequences, making it difficult for them to acknowledge that they have a problem that needs addressing.
Recognizing Signs of Alcohol Addiction in Different Settings


Home/Family Environment
Alcoholism and Family Dynamics
Alcohol addiction can have a big impact on a family’s dynamics. The unpredictable behavior, mood swings, and financial struggles brought on by the addiction may cause relationships to become strained. Conflicts and breakdowns in communication may increase, creating a tense and unhealthy environment at home.
Neglect of Parental Responsibilities
Parents struggling with alcohol addiction may neglect their parental duties and responsibilities. They might miss important events in their children’s lives, fail to provide emotional support, and even expose their children to risky situations or environments.
Workplace
Decreased Productivity
Alcohol addiction often results in decreased work performance and productivity. Individuals may struggle to concentrate, make decisions, or complete tasks on time. The quality of their work may suffer, leading to potential job loss or reprimands.
Absenteeism and Frequent Tardiness
Alcohol addiction can lead to absenteeism, where individuals frequently skip work without a valid reason. The effects of drinking or withdrawal symptoms may also cause them to be late for work or meetings.
Social Gatherings
Increased Tolerance for Alcohol
Alcohol-dependent individuals may exhibit a noticeably higher tolerance for alcohol than other people in social situations. They might consume large amounts of alcohol without showing signs of intoxication that would be expected in someone without a tolerance.
Risky Behaviors Under the Influence
Alcohol addiction can lead to impulsive and risky behaviors in social situations. This may include engaging in physical altercations, driving under the influence, or participating in other hazardous activities that they wouldn’t normally consider.


Get the help you deserve today. Start your journey to recovery by contacting us!
The Importance of Early Detection of Alcoholism
Benefits of Recognizing Signs of Alcohol Addiction Early
Improved Treatment Results
Early intervention for alcoholism increases the chances of effective treatment and recovery. Alcoholism becomes more ingrained the longer it is left untreated, making recovery harder.
Preservation of Physical Health
Early alcohol addiction detection can avoid or lessen the negative effects of long-term alcohol abuse on one’s physical health. This includes reducing the risk of liver damage, heart problems, and other related health issues.
Prevention of Psychosocial Impact
Alcohol addiction’s impact on mental health, interpersonal relationships, and general quality of life can be avoided or minimized with early detection. An early intervention can prevent the isolation that is frequently associated with addiction and help mend strained relationships.
Reduced Legal and Financial Consequences
Early intervention for alcohol addiction can reduce the likelihood of accidents, DUIs, and other legal problems, as well as the associated financial costs of court costs and medical expenses.
Enhanced Functioning in Daily Life
People who are just starting to develop an alcohol addiction may still be able to function in daily life to some extent. Early detection for alcoholism may be able to aid them in regaining control and reducing the disruptions brought on by addiction.
Consequences of Not Recognizing the Signs of Alcohol Addiction Timely
Health Deterioration
Without early identification of symptoms and signs of alcohol addiction can result in serious physical health problems like liver disease, cardiovascular issues, and irreversible organ damage.
Escalation of Mental Health Issues
Alcohol Addiction can worsen pre-existing mental illnesses and trigger the emergence of new ones, further complicating a person’s wellbeing.
Strained Relationships
Relationships may become stressed as a result of failing to recognize the early signs of alcohol addiction. Relationships with friends, with family, and in romantic relationships can all suffer permanent harm.
Legal and Financial Woes
The legal repercussions of alcohol addiction can worsen if left undetected, leading to criminal charges, license suspensions, and financial instability from fines and court costs.
Isolation and Loneliness
More people tend to isolate themselves from others as their addiction becomes more entrenched, which increases loneliness and makes it harder for them to find support.
Job Loss and Unemployment
Untreated alcohol addiction often leads to deteriorating job performance, which can ultimately result in job loss, unemployment, and financial hardship.
Heightened Risk of Accidents
Individuals who are in the later stages of their addiction are more likely to take risks by driving while intoxicated or participating in hazardous activities, which increases their risk of accidents and harm to both themselves and other people.
Seeking Help and Treatment Options
Overcoming alcohol addiction is a challenging journey, but seeking professional help can significantly increase the chances of a successful recovery journey from alcohol addiction. Encourage people to contact medical professionals, therapists, or addiction specialists if they think they may have an alcohol addiction. While acknowledging that taking this step requires courage, reassure them that they are not alone on this journey.
Treatment Options for Alcohol Addiction
Detoxification
Detoxification, often the first step in addiction treatment, involves safely removing alcohol from the body under medical supervision. Medical professionals can help manage the discomfort and keep an eye on the patient’s health because withdrawal symptoms can accompany this process.
Alcohol Addiction Rehab Programs
Programs for outpatient and inpatient rehabilitation offer individuals seeking recovery structured treatment environments. While outpatient programs enable people to participate in therapy while continuing to live at home, inpatient programs offer intensive care inside a facility. Typically, these programs combine counseling, therapy, and support groups.
Counseling and Therapy
Alcohol addiction can be successfully treated with behavioral therapies like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Motivational Enhancement Therapy (MET). They support people in understanding and altering their thought processes and drinking-related behaviors. Counseling sessions, both individual and group, offer a secure setting for dealing with underlying issues and learning coping mechanisms.
Alcohol Addiction Support Groups (e.g., Alcoholics Anonymous)
Support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) offer a caring community of people who are familiar with the struggles of alcohol addiction. These groups provide a venue for people to connect, offer support, and progress through the 12-step recovery program.
Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT)
Medications that reduce alcohol cravings and withdrawal symptoms may be beneficial for certain individuals. When combined with counseling, medication-assisted treatment can increase the likelihood of long-lasting recovery.
Holistic Approaches
By addressing the physical, emotional, and psychological aspects of addiction, holistic treatments like yoga, meditation, art therapy, and mindfulness exercises can supplement conventional approaches.
Aftercare and Relapse Prevention
Individuals who have completed initial treatment should consider enrolling in aftercare programs that provide ongoing support. These programs assist individuals in maintaining their recovery from alcohol addiction and developing relapse prevention strategies.
There is no one-size-fits-all cure for addiction; keep in mind that every person’s path to recovery is unique. It is crucial to find a treatment strategy that fits a person’s needs, preferences, and situation. To determine the most effective alcoholism prevention strategies, consulting your doctor is best.
Final Thoughts on Crucial Indicators: Recognizing the Signs of Alcohol Addiction
Alcohol use has various effects on our lives. It is essential to recognize the symptoms and signs of alcohol addiction so that those in need can receive assistance.
Identification of symptoms and signs of alcohol addiction is essential for a shift in mindset that enables people to face difficulties, get help, and rediscover their purpose. The first step in eradicating taboos is to acknowledge alcoholism as a medical condition and to provide support and understanding. Recognizing these signs of alcohol addiction demonstrates a commitment to human welfare and promotes open communication and empathy for healthier communities.
Interested in learning more? Read more related articles: The Long-Term Health Effects of Alcohol Addiction
Contact National Addiction Specialists For Your Recovery
Need Help?
If you are concerned about your alcohol use and would like to explore whether you might have AUD, National Addiction Specialists is here to help and support you!
Sources
Understanding Alcohol Use Disorder | National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA). (n.d.). Understanding Alcohol Use Disorder | National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA). https://www.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/brochures-and-fact-sheets/understanding-alcohol-use-disorder
Understanding Binge Drinking | National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA). (n.d.). Understanding Binge Drinking | National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA). https://www.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/brochures-and-fact-sheets/binge-drinking
The Cycle of Alcohol Addiction | National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA). (n.d.). The Cycle of Alcohol Addiction | National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA). https://www.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/cycle-alcohol-addiction
Alcohol use disorder – Symptoms and causes. (2022, May 18). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/alcohol-use-disorder/symptoms-causes/syc-20369243
D. (n.d.). Signs and Symptoms of Alcoholism. Drug Rehab. https://www.drugrehab.com/addiction/alcohol/alcoholism/signs-and-symptoms/
Symptoms of Alcohol Use Disorder – What is AUD? | NIAAA. (n.d.). Symptoms of Alcohol Use Disorder – What Is AUD? | NIAAA. https://www.rethinkingdrinking.niaaa.nih.gov/How-much-is-too-much/whats-the-harm/what-Are-Symptoms-Of-alcohol-Use-Disorder.aspx
What is an alcoholic? How to treat alcoholism. (n.d.). What Is an Alcoholic? How to Treat Alcoholism. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/157163
What are the Consequences of Drinking? – Rethinking Drinking | NIAAA. (n.d.). What Are the Consequences of Drinking? – Rethinking Drinking | NIAAA. https://www.rethinkingdrinking.niaaa.nih.gov/How-much-is-too-much/Whats-the-harm/What-Are-The-Consequences.aspx
Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism: Signs, Symptoms, and Diagnosis. (n.d.). Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism: Signs, Symptoms, and Diagnosis. https://www.healthline.com/health/alcohol-use-and-abuse
Symptoms of Alcohol Abuse. (2021, November 2). WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/mental-health/addiction/understanding-alcohol-abuse-symptoms