Understanding Sublingual Administration: A Direct Path to Better Treatment
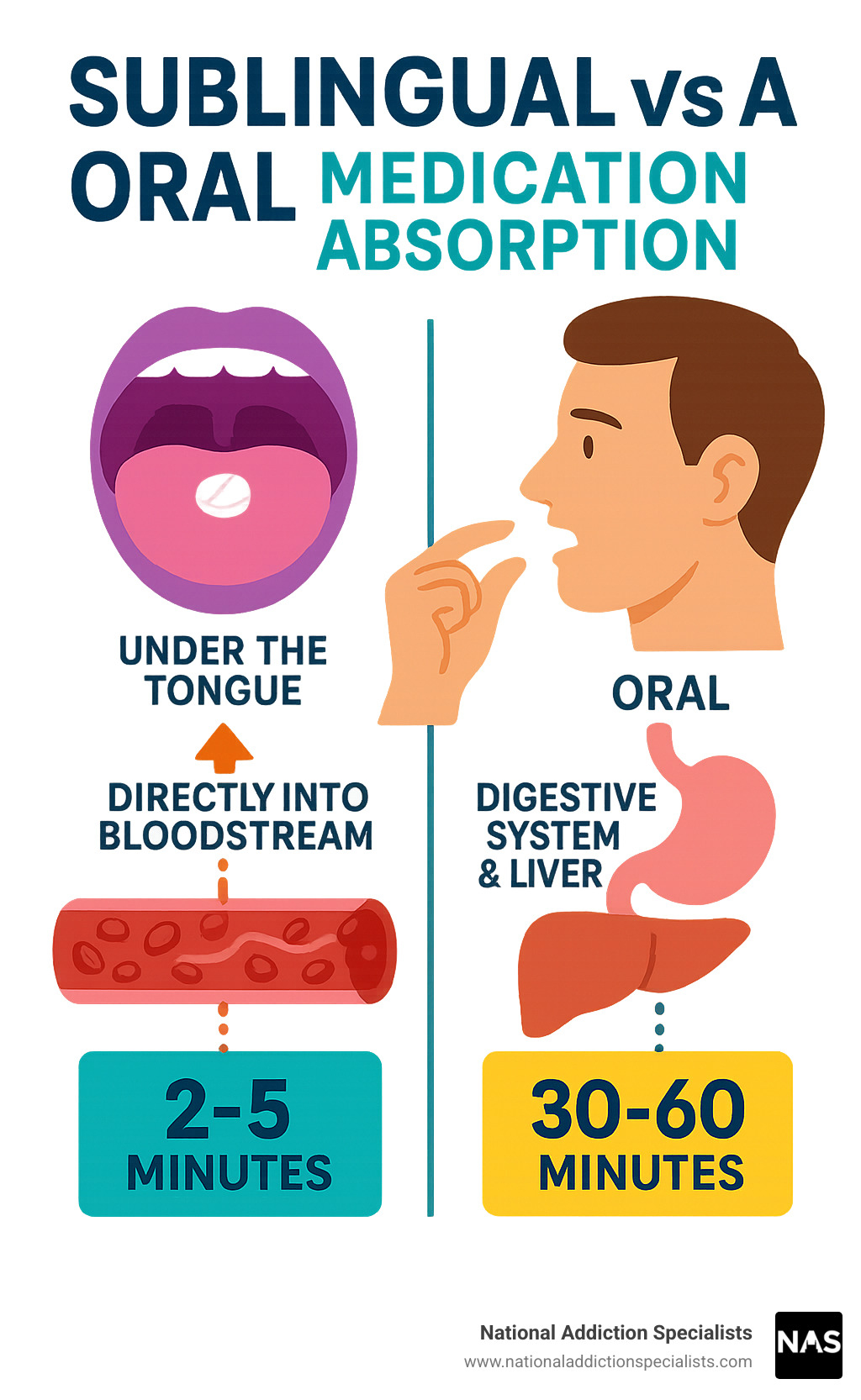
Sublingual administration is a method of taking medication by placing it under your tongue. It dissolves and enters the bloodstream directly through the mucous membranes, bypassing the digestive system for faster absorption and better results than traditional oral pills.
Quick Facts About Sublingual Administration:
- Definition: Medication placed under the tongue for absorption.
- Speed: Works within 2-5 minutes vs. 30-60 minutes for oral pills.
- Absorption: Direct into the bloodstream through capillaries under the tongue.
- Benefits: Bypasses liver metabolism, faster action, lower doses may be needed.
- Common forms: Tablets, films, sprays, and drops.
- Best for: Emergencies, patients who can’t swallow, and addiction treatment.
The sublingual route avoids the “first-pass effect,” where drugs are broken down by the stomach and liver before reaching the bloodstream. This allows for greater absorption and is particularly valuable in addiction medicine. For example, understanding how buprenorphine works is key to appreciating its effectiveness in suboxone treatment for opioid use disorder.
I am Dr. Chad Elkin, founder of National Addiction Specialists. I have found that sublingual medications transform patient care, especially in addiction treatment where rapid, reliable absorption is critical for success.
How Sublingual Differs from Other Routes
Medication can be administered in many ways, but sublingual (under the tongue) and buccal (between cheek and gum) routes are unique. They offer direct absorption into the bloodstream, avoiding the digestive system and the liver’s “first-pass effect,” which can break down a significant portion of a drug. This leads to a faster onset of action and higher bioavailability (more of the drug is available to the body).
Let’s compare common administration routes:
| Feature | Sublingual | Buccal | Oral | Intravenous |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placement | Under the tongue | Between cheek and gum | Swallowed | Into a vein |
| Onset of Action | Very fast (minutes) | Fast (minutes) | Slower (30-60+ min) | Immediate (seconds) |
| First-Pass Metabolism | Bypassed | Bypassed | Significant | Bypassed |
| Bioavailability | High | High | Variable | 100% |
| Ease of Use | High (self-administered) | High (self-administered) | High (self-administered) | Requires professional |
| Patient Comfort | High (non-invasive) | High (non-invasive) | High (non-invasive) | Moderate (needle) |
The Science Behind Sublingual Administration
The area under your tongue is rich with tiny blood vessels called capillaries. When a sublingual medication is placed there, it dissolves and passes through the thin mucous membrane directly into the bloodstream.
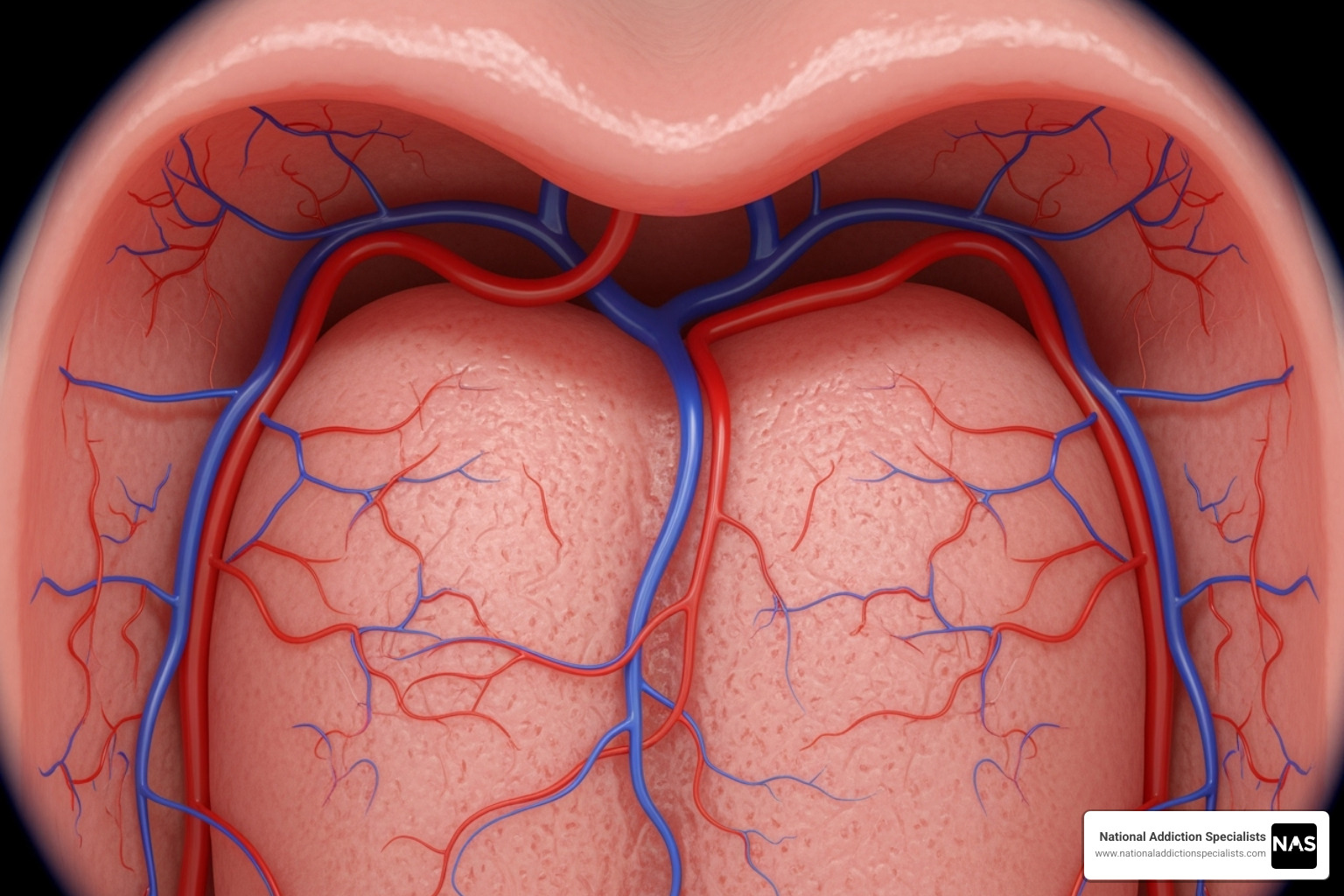
This direct route is special because it completely bypasses the liver’s initial processing, known as the first-pass effect. The liver filters and breaks down substances, which can reduce a medication’s effectiveness, sometimes by up to 90%. By skipping this step, sublingual administration leads to a faster onset of action (minutes vs. 30-60 minutes for oral pills) and higher bioavailability, meaning more of the drug reaches your system. This science is why medications like buprenorphine are formulated for sublingual use in addiction treatment. You can find more info about Suboxone for Opioid Addiction to see how this translates to successful treatment.
When is this Method Prescribed?
Doctors choose the sublingual route in specific situations where it offers a clear advantage:
- Emergency situations: For conditions like a heart attack, sublingual nitroglycerin provides relief in minutes.
- Severe pain: Rapid relief for breakthrough cancer pain or other intense conditions.
- Swallowing difficulties (dysphagia): An effective alternative for elderly patients or those with medical conditions that make swallowing pills difficult or impossible.
- Nausea and vomiting: Bypasses the stomach, ensuring medication is absorbed even if a patient can’t keep things down.
- Poor stomach absorption: For drugs that are degraded by stomach acid or are not well-absorbed in the digestive tract.
- Opioid use disorder treatment: Medications like buprenorphine have poor oral bioavailability and work best when absorbed sublingually, ensuring consistent effects to manage recovery.
Factors Affecting Absorption
While effective, several factors can influence sublingual absorption. To get the most from your treatment, be mindful of the following:
- Saliva production: Medication needs saliva to dissolve. If you have dry mouth, a small sip of water before taking the dose can help.
- Eating or drinking: Avoid eating, drinking, or rinsing your mouth until the medication has completely dissolved, as this can wash it away or cause you to swallow it.
- Smoking: Tobacco can constrict blood vessels and alter the mucous membranes in your mouth, reducing absorption. Avoid smoking before and after your dose.
- Mouth sores: Irritation or sores can interfere with absorption. Discuss any oral health issues with your provider.
- Medication properties: Not all drugs are suitable for this route. Factors like molecular size and potency determine if a drug can be formulated for sublingual use. For more details, you can explore resources on drug absorption factors.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Sublingual and Buccal Medications
Like any treatment, sublingual and buccal medications have unique benefits and challenges.
The primary advantage is rapid action. By bypassing the digestive system and entering the bloodstream directly, these medications can work in minutes, which is critical for emergencies like chest pain or for managing severe breakthrough pain.
Another benefit is increased potency and the potential for lower doses. Since the medication avoids the liver’s first-pass metabolism, more of the drug is available to the body. This can lead to fewer side effects. The convenience of self-administration without needles and the comfort for those who cannot swallow pills or have stomach issues are also significant advantages.
Make an Appointment to Treat Addiction
Please don’t hesitate. Make an appointment today.
Make an Appointment to Treat Addiction
Key Advantages of the Sublingual Route
To summarize, the sublingual route is valuable for several key reasons:
- Quick relief: Provides relief in minutes for acute conditions like angina or panic attacks.
- Bypasses liver metabolism: Avoids the first-pass effect, preserving the drug’s active ingredients.
- Avoids stomach irritation: A gentler option for those with sensitive stomachs or for drugs degraded by stomach acid.
- Helps patients who can’t swallow pills: An essential alternative for patients with dysphagia, nausea, or other swallowing difficulties.
These advantages are crucial in addiction treatment. You can learn more about the Benefits of Suboxone Treatment for Opioid Addiction to see how this method supports recovery.
Potential Disadvantages and Risks
Despite the benefits, there are potential drawbacks:
- Incorrect administration: Accidentally chewing or swallowing the medication makes it less effective.
- Limited drug suitability: Not all drugs can be absorbed this way due to their size, taste, or potential for irritation.
- Unpleasant taste: Some sublingual drugs have a bitter or metallic taste that can be difficult for patients to tolerate.
- Mouth irritation: Long-term use may cause sores or sensitivity in the delicate tissues under the tongue.
- Interference: Eating, drinking, or smoking before or after taking the medication can significantly reduce its effectiveness.
A Patient’s Guide to Using Sublingual Medication
Taking sublingual medication is straightforward once you know the steps. These medications come in several forms, all designed to dissolve quickly under your tongue.

- Tablets: Small, compressed pills, like nitroglycerin for chest pain.
- Films: Thin, dissolvable strips, like Suboxone, which is used in opioid recovery programs.
- Sprays and Drops: A fine mist or concentrated liquid, sometimes used for vitamins like B12.
Many types of medications are available in sublingual form, including opioids like buprenorphine, benzodiazepines for anxiety, cardiovascular drugs, and even some vitamins and steroids.
Proper Technique for Taking Sublingual Medication
Getting the technique right is essential for the medication to work correctly.
- Wash your hands and sit upright.
- Place the medication under your tongue. For buccal medication, place it between your cheek and gum.
- Do not chew, suck, or swallow the medication. Let it dissolve naturally.
- Allow it to dissolve completely, which usually takes a few minutes. Try not to talk during this time.
- Avoid eating or drinking for 15-30 minutes after the medication has dissolved to ensure full absorption.
- Follow your pharmacist’s specific instructions, as some medications may have unique requirements.
What to Discuss with Your Doctor
Open communication with your provider ensures your treatment is safe and effective. Be sure to discuss:
- All current medications: Include over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
- Smoking habits: Smoking can reduce absorption and may require adjustments to your treatment plan.
- Oral health: Issues like dry mouth, mouth sores, or gum disease can interfere with absorption.
- Swallowing difficulties: Let your doctor know if you have trouble swallowing pills.
- Potential side effects: Ask what to expect so you know what is normal.
- Missed doses: Understand the protocol for your specific medication if you miss a dose.
For patients in recovery, these conversations are vital. You can find more answers in our Suboxone Treatment FAQ.
Frequently Asked Questions about Sublingual Administration
Here are answers to some of the most common questions patients have about sublingual medications.
Can all medications be taken sublingually?
No. A drug’s suitability for sublingual administration depends on several factors:
- Molecular size: Molecules must be small enough to pass through the mucous membrane.
- Taste: The medication must be palatable enough to hold in the mouth while it dissolves.
- Irritation potential: The drug cannot be harsh or damaging to the delicate tissues in the mouth.
- Dose size: The required dose must be small enough to fit in a tablet or film that dissolves comfortably.
- Release mechanism: This route is for rapid absorption, not for drugs that require slow, sustained release.
How long does it take for sublingual medication to work?
Sublingual medication works very quickly, typically within 2-5 minutes. Because it is absorbed directly into the bloodstream, it bypasses the entire digestive system, avoiding the 30-60 minute delay common with oral pills. This rapid onset is why it’s so valuable for emergencies and for managing acute symptoms like cravings in addiction treatment.
What happens if I accidentally swallow a sublingual pill?
If you accidentally swallow a sublingual medication, don’t panic. It will be absorbed through your digestive system like a regular oral pill. However, this means you will likely experience a slower onset of action and reduced effectiveness. The drug will be exposed to stomach acid and liver metabolism (the “first-pass effect”), which can significantly break it down. For some medications like buprenorphine, swallowing it renders it almost completely ineffective.
Do not take an extra dose unless specifically instructed by your healthcare provider, as this could be dangerous. Contact your doctor for guidance.
Your Path to Recovery with Modern Treatment
Sublingual administration is a key advance in modern medicine, especially in addiction treatment. This delivery method allows medications like buprenorphine to work quickly and reliably, providing a stable foundation for recovery from opioid use disorder.
At National Addiction Specialists, we use these evidence-based methods to provide effective care. Our telemedicine platform brings this treatment directly to your home in Tennessee and Virginia, offering a convenient and confidential path to recovery. We accept both Medicaid and Medicare to ensure care is accessible.
Recovery is possible. Our personalized plans combine sublingual medication with comprehensive counseling to support you. If you are ready to take the first step, our expert providers are here to help with compassion and expertise. Learn more about our Suboxone Treatment Programs and find how modern treatment can change your life.
This article was medically reviewed by:
Chad Elkin, MD, DFASAM is a board-certified addiction medicine physician, founder, and Chief Medical Officer of National Addiction Specialists, dedicated to treating substance use disorders. A Distinguished Fellow of the American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM), Dr Elkin currently serves as President of the Tennessee Society of Addiction Medicine (TNSAM) and has held various leadership roles within the organization. Dr Elkin chairs ASAM’s Health Technology Subcommittee and is an active member of its Practice Management and Regulatory Affairs Committee, State Advocacy and Legislative Affairs Committee, and other committees. He also serves on the planning committee for the Vanderbilt Mid-South Addiction Conference. Committed to advancing evidence-based policy, Dr Elkin is Chairman of the Tennessee Association of Alcohol, Drug, & Other Addiction Services (TAADAS) Addiction Medicine Council, which collaborates with the TN Department of Mental Health & Substance Abuse Services (TDMHSAS). He has contributed to numerous local, state, and national task forces, helping develop professional guidelines, policies, and laws that align with best practices in addiction medicine. His work focuses on reducing addiction-related harm, combating stigma, and ensuring access to effective treatment. Passionate about the field of addiction medicine, he remains dedicated to shaping policy and enhancing patient care.
Suboxone® and Subutex® are a registered trademark of Indivior UK Limited. Any mention and reference of Suboxone® and Subutex® in this website is for informational purposes only and is not an endorsement or sponsorship by Indivior UK Limited.